What is a Locked Differential?
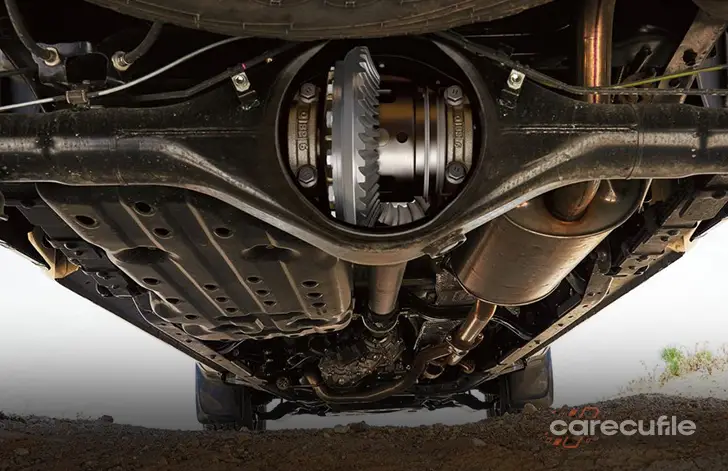
Locked differential is used in vehicles produced for a specific purpose, which is not present in normal vehicles. The purpose of the locked differential is to correct the torque distribution imbalance that the open differential makes torque under normal conditions, and to ensure that there is no speed difference between the two wheels. In the open differential, there are obvious speed differences between the vehicle wheels, we can exemplify this speed difference as follows. Another example is the difference in cornering. While turning the corner, the wheel remaining inside the bend turns faster and the difference is created here.
Vehicles with a locked differential are generally vehicles produced for specific purposes. The first of these are formula 1 cars. As everyone knows, the most necessary thing for formula cars is speed and efforts are made for minimum speed loss. The locked differential is one of them. Thanks to this system, formula 1 vehicles experience less speed loss during turns and their handling becomes more comfortable. In this way, they will not go off the road and they will not lose their speed. Another example is off-road vehicles. These vehicles have a locked differential for handling. For example, if the vehicle sinks into the mud while on the road, in vehicles with an open differential system, the wheel in the mud turns at full speed and this will be to your detriment. Instead, with the locked differential, equal torque is provided to both wheels, and with this, the traction of the vehicle in that case increases and it gets rid of the mud.